Double sided pcb Normal pcb Lead free HASL Counterbore Manufacturer | YMS PCB
HAL(Lead Free), the full name is Hot Air leveling with Lead Free. Compared with HASL, the main difference for HAL(Lead Free) is the element of material which do not contain Lead(Pb), so it’s RoHS Compliant and it’s much more popular and widely used in производства .
HAL(Lead Free) requires higher run temperatures for lead free solder and longer contact time, the production cost for HAL(Lead Free) is slightly higher than HASL(Tin/Lead).
The manufacturing process of HAL(Lead Free) is similar to HASL(Tin/Lead), the circuit boards will be submersed in molten solder(Lead Free). This solder will cover all the exposed copper surfaces. Upon retraction from the solder, high pressure hot air is blown over the surface through air knives, this levels the solder deposit and removes the excess solder from the surface of printed circuit boards.
Печатная плата Введение
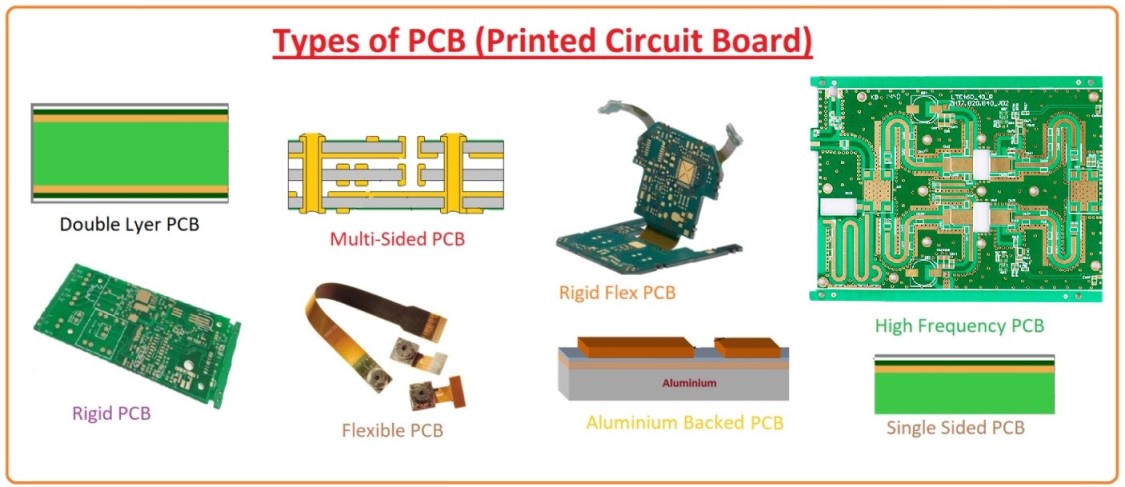
Обычная печатная плата: Most PCBs for simple electronics are simple and composed of only a single layer. More sophisticated hardware such as computer graphics cards or motherboards can have 2 or multiple layers, sometimes up to twelve.
A printed circuit board (PCB) mechanically supports and electrically connects electrical or electronic components using conductive tracks, pads and other features etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto and/or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. Components are generally soldered onto the PCB to both electrically connect and mechanically fasten them to it.PCBs can be single-sided (one copper layer), double-sided (two copper layers on both sides of one substrate layer), or multi-layer (outer and inner layers of copper, alternating with layers of substrate). Multi-layer PCBs allow for much higher component density, because circuit traces on the inner layers would otherwise take up surface space between components. The rise in popularity of multilayer PCBs with more than two, and especially with more than four, copper planes was concurrent with the adoption of surface mount technology.
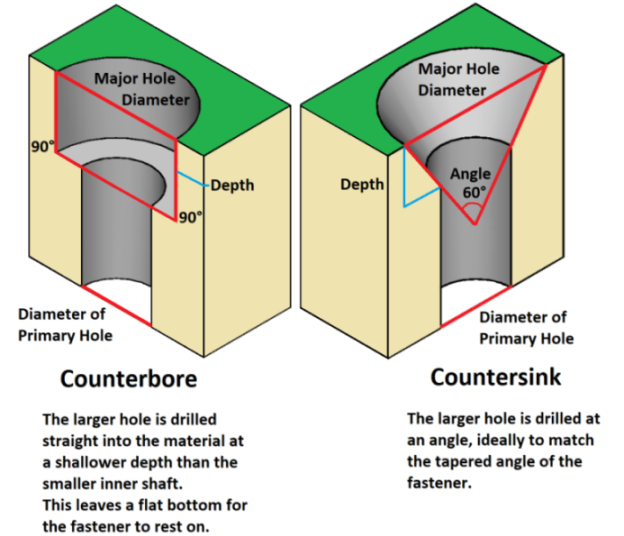
What is the difference between a Countersink and a Counterbore?
Возможности производства YMS Normal PCB:
| Обзор возможностей производства обычных печатных плат YMS | ||
| Характерная черта | возможности | |
| Количество слоев | 1-60л | |
| Доступная обычная технология печатных плат | Сквозное отверстие с соотношением сторон 16: 1 | |
| похоронен и слеп через | ||
| Гибридный | Высокочастотный материал, такой как RO4350B, FR4 Mix и т. Д. | |
| Высокоскоростной материал, такой как M7NE, FR4 Mix и т. Д. | ||
| Материал | СЕМ- | CEM-1; CEM-2, CEM-4, CEM-5. и т. Д. |
| FR4 | EM827, 370HR, S1000-2, IT180A, IT158, S1000 / S1155, R1566W, EM285, TU862HF, NP170G и др. | |
| Высокоскоростной | Megtron6, Megtron4, Megtron7, TU872SLK, FR408HR, N4000-13 Series, MW4000, MW2000, TU933 и др. | |
| Высокая частота | Ro3003, Ro3006, Ro4350B, Ro4360G2, Ro4835, CLTE, Genclad, RF35, FastRise27 и т. Д. | |
| Другие | Полиимид, Tk, LCP, BT, C-ply, Fradflex, Omega, ZBC2000, PEEK, PTFE, на керамической основе и т. Д. | |
| Толщина | 0,3 мм-8 мм | |
| Максимальная толщина меди | 10 унций | |
| Минимальная ширина линии и расстояние | 0,05 мм / 0,05 мм (2 мил / 2 мил) | |
| BGA PITCH | 0,35 мм | |
| Мин. Размер механического сверления | 0,15 мм (6 мил) | |
| Соотношение сторон сквозного отверстия | 16 : 1 | |
| Чистота поверхности | HASL, бессвинцовый HASL, ENIG, иммерсионное олово, OSP, иммерсионное серебро, золотой палец, гальваническое покрытие твердого золота, выборочный OSP , ENEPIG.etc. | |
| Через параметр заполнения | Переходное отверстие покрывается гальваническим покрытием и заполняется проводящей или непроводящей эпоксидной смолой, затем закрывается и покрывается (VIPPO) | |
| С медным наполнением, с серебряным наполнением | ||
| Регистрация | ± 4 мил | |
| Паяльная маска | Зеленый, красный, желтый, синий, белый, черный, фиолетовый, матовый черный, матовый зеленый и т. Д. | |
Вам может понравиться:
1. Summary of matters needing attention in circuit board welding
3 、What is PCB
4、Что такое тестирование голой платы?
5. Что такое конструкция высокочастотной печатной платы
Узнать больше о продуктах YMS