There are various flex circuit boards. Normally, they are designed according to diverse configurations and specifications. It's worth pointing out that they are also categorized based on layers. Let's get to understand the different types of flex circuit boards based on configurations and on layers. Flexible Circuit Boards Classification Based on Layers
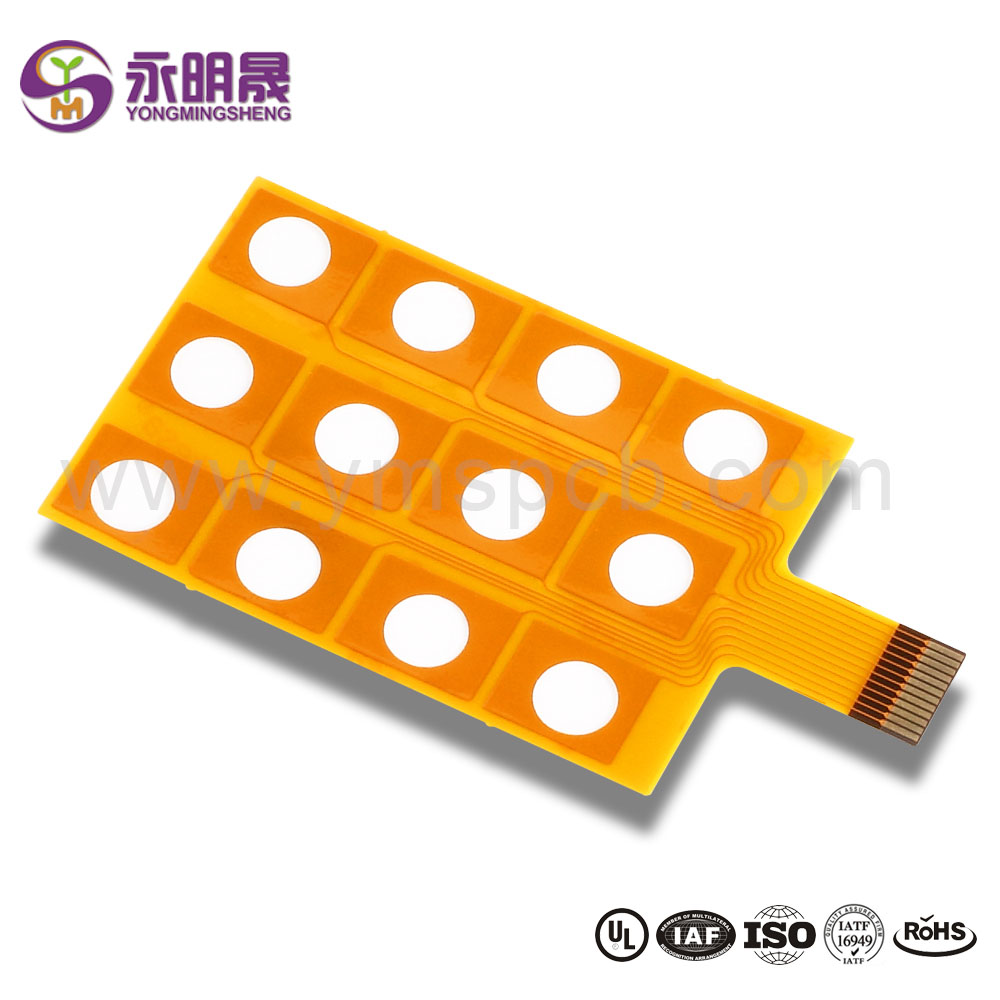
Single-Sided Flexible Circuit Boards
This is among the basic types of flexible circuit boards based on layers. It contains a single layer of polyimide film. It also has a slim layer of copper.
Single-Sided Flexible Circuit Boards with Dual Access
Just like the name suggests, these circuit boards are single-sided but have the copper sheet accessible from both sides.
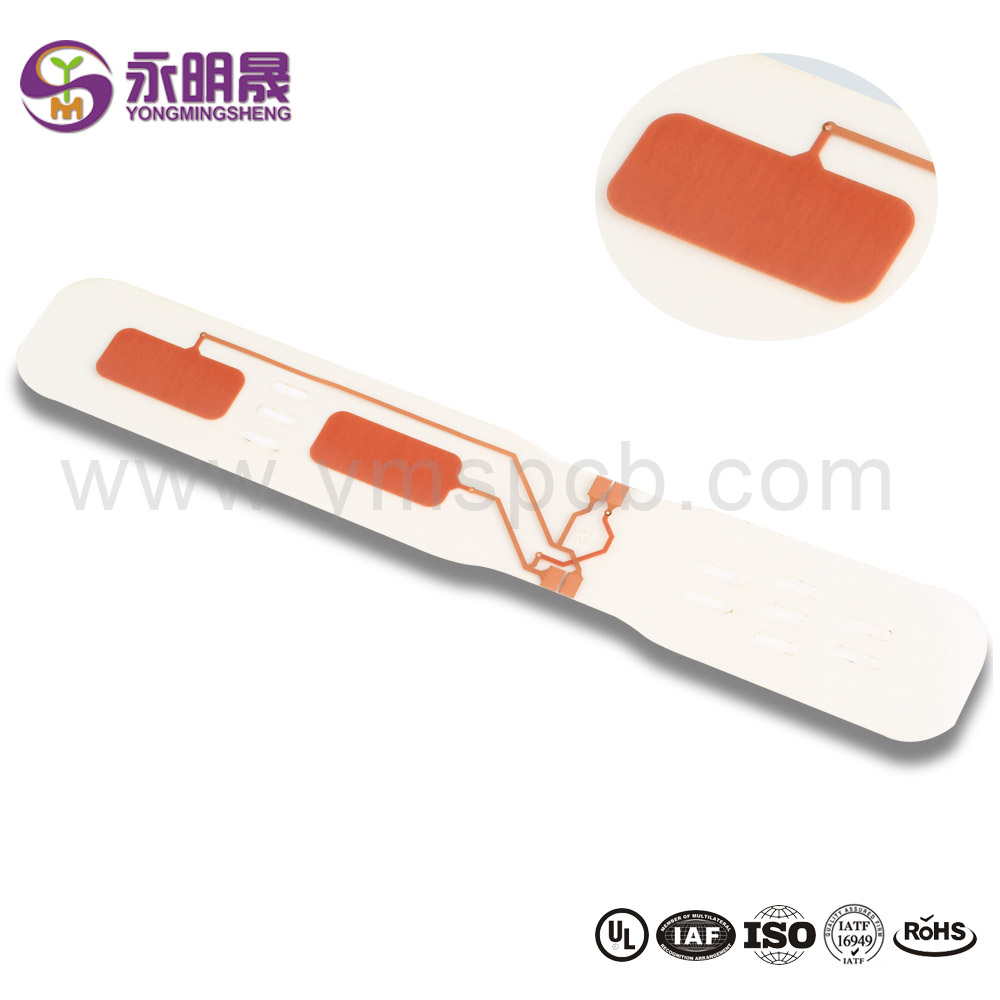
Double-Sided Flexible Circuit Boards
These particular circuit boards contain a double layer of conductors on either side of the polyimide layer.
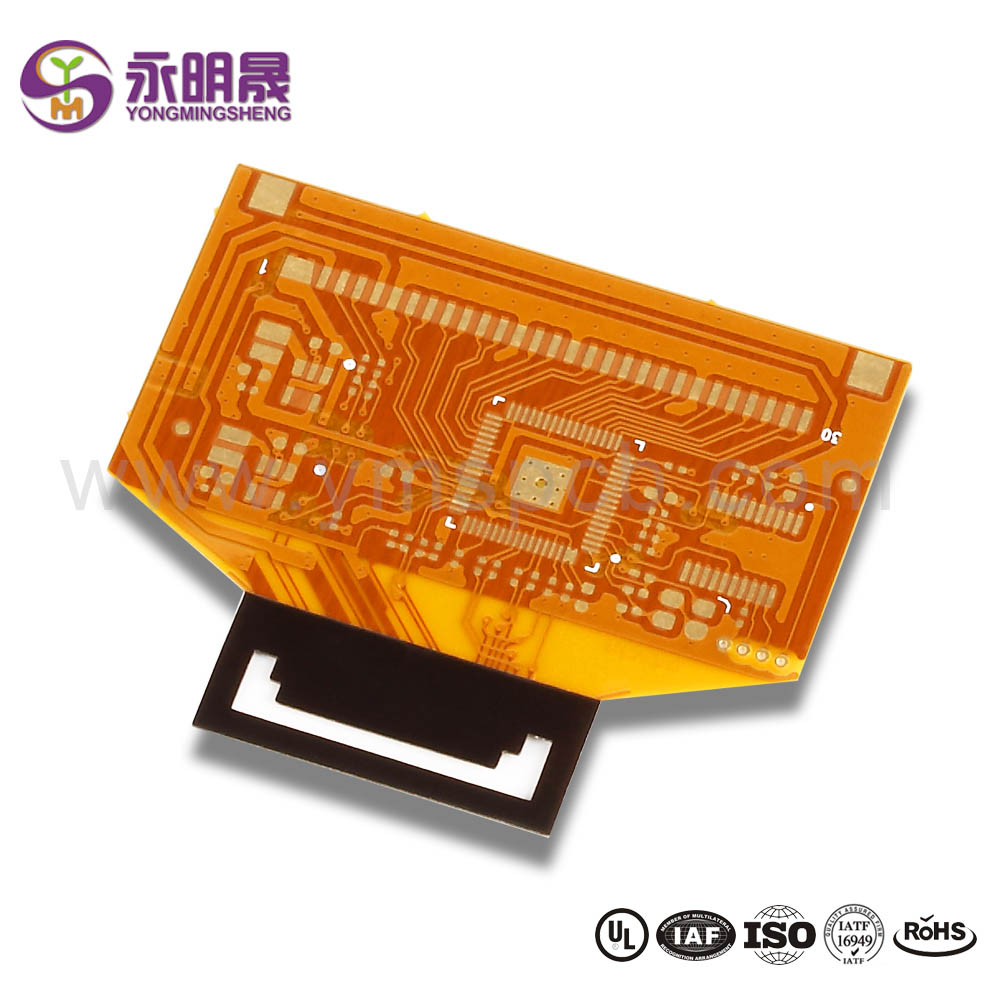
Multi-Layered Flexible Circuits
This circuit contains a combination of double-sided and one-sided flexible circuits.
Based on the afore-mentioned types of flexible circuit boards, it is evident that designers and engineers have a wider spectrum of selection for different applications. It is this flexibility that makes flexible circuit boards highly beneficial.
(1) FPC base material:
The commonly used material for flexible circuit boards is polyimide (POLYMIDE), which is a high-temperature, high-strength polymer material. It is a polymer material invented by DuPont, and the polyimide produced by DuPont is called KAPTON. You can also buy some polyimides produced in Japan at a lower price than DuPont.
It can withstand a temperature of 400 degrees Celsius for 10 seconds, and its tensile strength is 15,000-30,000 PSI.
The 25μm thick FPC substrate is the cheapest and the most common application. If the flexible circuit board needs to be harder, a 50μm substrate should be used. Conversely, if the flexible circuit board needs to be softer, a 13μm substrate is used.
(2) Transparent glue for FPC substrate:
There are two types of epoxy resin and polyethylene, both of which are thermosetting adhesives. The strength of polyethylene is relatively low. If you want the circuit board to be softer, choose polyethylene.
The thicker the substrate and the transparent glue on it, the harder the circuit board. If the circuit board has a relatively large bending area, you should try to use a thinner substrate and transparent glue to reduce the stress on the surface of the copper foil, so that the chance of micro-cracks in the copper foil is relatively small. Of course, for such areas, single-layer boards should be used as much as possible.
(3) FPC copper foil:
There are two types: rolled copper and electrolytic copper. Rolled copper has high strength and bending resistance, but the price is more expensive. The price of electrolytic copper is much cheaper, but its strength is poor and it is easy to break. It is generally used in occasions where it is rarely bent.
The thickness of the copper foil should be selected according to the minimum lead width and minimum spacing. The thinner the copper foil, the smaller the minimum achievable width and spacing.
When choosing rolled copper, pay attention to the rolling direction of the copper foil. The rolling direction of the copper foil should be the same as the main bending direction of the circuit board.
(4) Protective film and its transparent glue:
Similarly, a 25μm protective film will make the flexible circuit board harder, but the price is cheaper. For circuit boards with relatively large bends, it is best to choose a 13μm protective film.
Transparent glue is also divided into epoxy resin and polyethylene, and the circuit board using epoxy resin is relatively hard. After the hot pressing is completed, some transparent glue will be extruded from the edge of the protective film. If the size of the pad is larger than the opening size of the protective film, the extruded glue will reduce the size of the pad and cause its edges to be irregular. At this time, transparent glue with a thickness of 13μm should be used as much as possible.
(5) pad plating:
For circuit boards with relatively large bending and exposed pads, electroplated nickel + electroless gold layer should be used, and the nickel layer should be as thin as possible: 0.5-2μm, and the chemical gold layer 0.05-0.1μm.
Learn more about YMS products
People also ask
Post time: Dec-29-2021