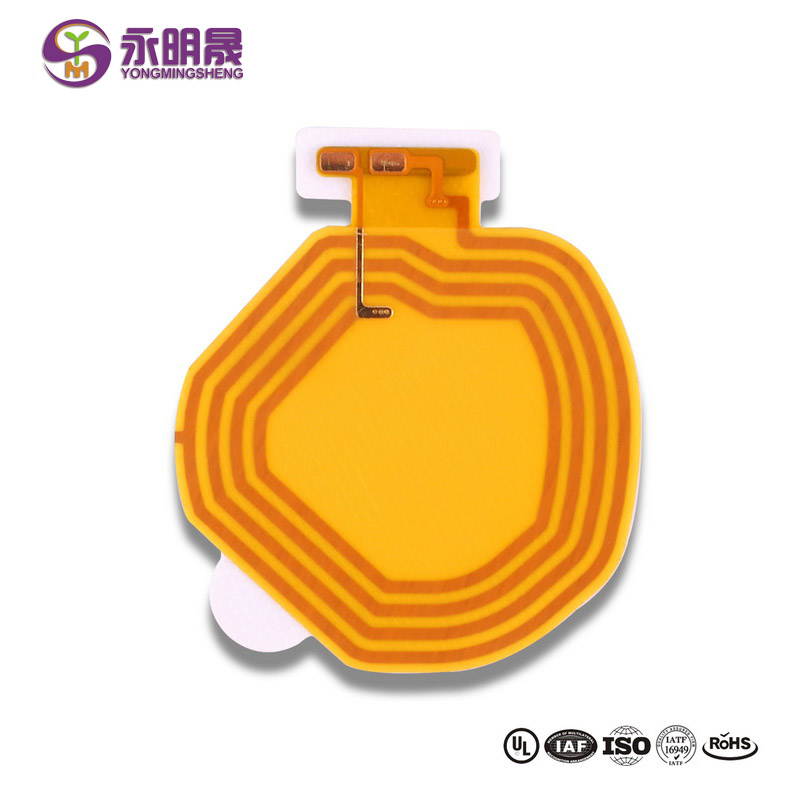
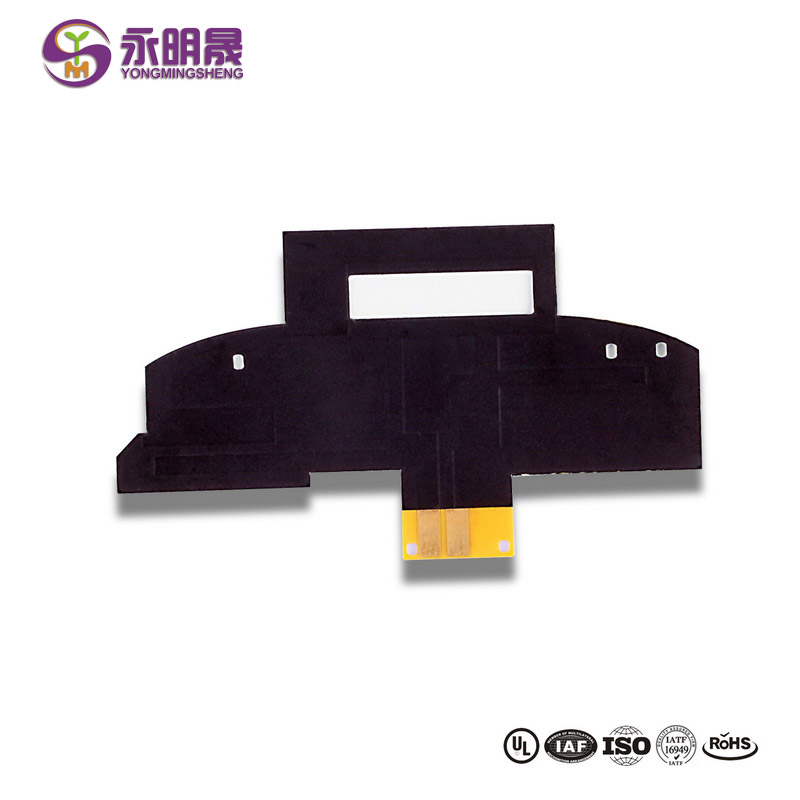
Single-Sided Flexible PCB
Why Choose YMSPCB for Your Single-Sided Flexible PCB
Single-sided flexible PCB or single-sided flex PCB is the most basic flexible circuit board. The technology of single-sided flexible PCB is also the most simple in the flex PCB industry.
As a leading single-sided flexible PCB manufacturer in China, YMSPCB can offer a turnkey solution for your project. From PCB design & layout, and PCB fabrication to PCB assembly, all processes are in-house and not outsourcing.
The quality is under our control, meanwhile, we can assure the delivery time.
If you have one project that needs to be produced in a hurry, YMSPCB can help you to make it. We can produce the prototype of a single-sided flexible PCB within 24H and ship it by UPS, FedEx, or DHL.
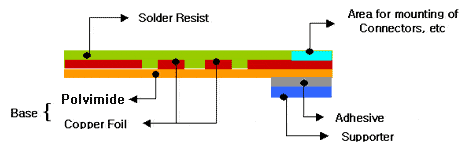
Single-sided flexible PCB has one conductive copper layer and one coverlay.
The standard board thickness is 1/2mil to 3mil and the copper thickness is 1/3oz to 2oz.
We have full service for quick-turn jobs and state-of-the-art equipment. lt can meet your complicated project deadlines and budgets.
There are many different applications for single-sided flexible PCB, such as barcode equipment.
cameras, smartphones, GPS systems, motion systems, and Satellites.
Are you looking for a premier single-sided flexible PCB supplier? YMSPCB is your best choice. YMSPCB has over 200 workers in our workshop and the monthly capacity is 40.000 sauare meters.
When you have any single-sided flexible PCB inquiry, please send it to us.
Single-Sided Flexible PCB
We put at your disposal our know-how for the most complex printed circuit designs with parameters or characteristics so special that they require the personal assistance of our team. We will provvide customized solutions that meet your needs simply by sending us your files by e-mail.



Single-Sided FlexiblePCB: The Ultimate FAQ Guide
The most basic kind of flexible circuit is a single-sided flexible PCB, also known as a single-sided FlexPCB.
They're made up of a lightweight dielectric film that's been laminated to a single copper layer.
After that, the copper coating is chemically engraved to fit the circuit pattern style. For improved insulation and safety, polyimide cover layers may be added to the circuit board.
A single-sided flexible PCB is a type of circuit board that consists of a flexible polyimide film laminated a thin sheet of copper.
This Circuit is also known as single-layer flex. Then The copper layer is chemically etched to produce a circuit pattern specific to your specific design requirements.
In this circuit, Polyimide overlay is added for insulation and environmental protection of this circuit
One conductive copper layer and bonded between two insulating layers of polyimide/coverlay/copper/flex core is added in this layer. Flex Core Materials are :
Standard thicknesses: % mil to 3 mils in either adhesive or adhesiveness constructions.
Standard copper thicknesses: 1/3 oz to 2 oz in rolled annealed or electrodeposited formats.
Its Coverlays Standard thickness is 1/2 mil to 2 mil polyimide, with 1/2 mil to 2 mil epoxy or acrylic adhesive.
A single conductive copper sheet is bonded between two insulation layers or one polyimide insulating layer, and an exposed side is used in the one-sided flexible PCB configuration.
After that, the circuit outline is carved out of the internal copper sheet using a chemical etching technique.
Components, cables, pins, and stiffeners may all be seen on single-sided flex PCB boards. Similarly, certain single-sided flexible PCBs feature a dual-access mechanism that enables access to the conduction material from both sides of the circuit.
This design purpose necessitates a compact PCB and specialized layers to create access for the single copper layer via the base material's polyimide layer.
Several considerations go into developing a modular PCB layout, from materials to vias. Here are several considerations to consider when you build a single-sided flexible PCB layout.
1. Always consider the operating environment in which the final product has to function. The layout design process and materials differ for non-extreme environments and extreme environments.2. Bear in mind the perfect bend ratio, which is the relationship between the bend radius and the flexible circuit's thickness. The greater the bend radius, the greater the risk of failure while flexing.3. Conductor selection and optimum routing techniques are essential since the path that transmits electrical current from one point to another decides PCB efficiency. The conductor pattern can also be studied to determine how flexing affects it. Conductors can be routed as near as possible across the bend
Zones.
4. Pad fillets are recommended where the pad diameter is larger than the connecting strand width because they increase etched yield and material power.5. Attempt to remove tear relief. A relief slot and an expansive corner radius are two popular strategies for avoiding tears in flex circuits.
6. Choose between blind or buried vias carefully because they considerably affect the cost of the single-sided flexible PCB.
7. Use mechanical stiffeners with caution since they will stiffen the SMT, connector, and other places on your flexible PCB.8. Regardingimpedance regulation and signal integrity, reference plane layers and shielding are critical a typical shielding form, solid copper improves the circuit's rigidity and should be included in the thickness-to-bend radius analysis. Some shielding techniques, such as cross-hatching and silver ink. may be used to improve flexibility.9. Maintain signal integrity and impedance control The amount and speed at which electricity will flow down a trace are referred to as impedance. The proper operation of your signals and the entire circuit board is referred to as matching impedance. The trace width, the size of the paths in the reference plane lavers, the thickness of the traces, and the distance between two tracks in various impedance applications are all variables that influence the impedance feature of a flexible circuit.10. Before exposing the single-sided flexible circuit to extreme temperatures, it's crucial to guarantee that all moisture has been eliminated. After baking, quickly process the flex circuits. lf this isn't practical, keep the circuits in a nitrogen chamber or a desiccant-filled sealed dry box.
The requirements imposed on a single-sided flexible circuit stack layout must be met continuously over the product's existence.
The material must also fit together with the other layers of the flexible circuit stack to maintain the simplicity of manufacturing and durability.
The primary layers of the flex circuit stack and their roles are defined in the following subsections
Base Material
The lightweight polymer film that acts as the laminate's basis is regarded as the base material.
lt is liable for the bulk of the flexible circuit's critical physical and electrical properties.
The base material contains many of the signature properties of adhesive-free circuit construction
Thinner materials are more flexible than thicker materials and are used in a wide variety of thicknesses.
The material hardness is proportional to the cube of the thickness, which means that doubling the thickness renders the material eight times stiffer and still deflects 1/8 as much under the same load
Modern thin-film technology allows the production of ever-smaller circuitry at a lower cost and with greater efficiency.
Bonding Adhesive
Adhesives serve as bonding agents for laminates, but they are still an essential component of the circuit's dielectric structure.
A flexible PCB is produced with a laminate, which is a metal-clad film. Because of their low-temperature tolerance, adhesives often restrict laminate efficiency, particularly when polyimide is used as the base material.
Many adhesives have a lower temperature capacity than thermoplastic polyimides. Also, with elevated temperatures and loads, many of them can soften. The thermoplastic/thermoset polyimides that withstand movement are the best-performing modern products.
In interconnection applications, the real benefits of flexible circuits compared to conventional cabling and rigid PCBs include:
Reduced cabling and wiring errors
Elimination of mechanical connectors
Enhanced design flexibility
Higher circuit density
More robust operating temperature range
Stronger signal quality
improved reliability and impedance control
Size and weight reduction
There are two elementary types of applications for flexible circuits
Static Applications
This type is known as flex-to-ft, and in this type, flexing is not frequent. Flex circuits are installed to adapt to a particular application in this application. it's best described as a one-time bending.
Dynamic Applications
In this type, flexing is quite frequent. it is used in applications in which the flexible circuit needs to be bent multiple times as part of the application functionality.
In essence, Electronics such as calculators, mobile phones, scanners, cameras, and LCD televisions utilize flex circuits.
They're used in cardiac monitors, pacemakers, and hearing aids in the medical industry. They're used to create robotic weapons, sorting robots, and barcode scanners, among other items. Satellites, GPS devices, high-density connectors, high-speed chip-to-chip interconnection, and solar cells all utilize them.
Although flexible circuits have been used in various items, the most valuable has been their medical device usage.
They have given life-changing advantages to people with different medical conditions. The use of flex circuits in clinical applications can be classified into the following categories:
Flexible circuits are used as a means of interconnection for the packaging and interconnection of an electronic assembly such as portable monitors and implantable devices.
Flexible circuits are interfacing with the patient to provide diagnostics and therapy.
Hearing aids such as cochlear implants
Ultrasound and RF therapy
Heart disease diagnostics, implants, and treatments such as pulse makers.
If you cannot find an answer to your question in our FAQ, you can always contact us and we will be with you shortly.
